
Modification times and permissions of extracted directories are set when all files from this directory are extracted. Using -checkpoint-action without -checkpoint will assume the default checkpoint interval of 10 records.ĭelay setting modification times and permissions of extracted directories until extraction has ended. The supplied actions will be executed in the order of their appearance on the command line. Several -checkpoint-action options can be specified. Output string on the current console (' /dev/tty'). ACTION may be one of the following:ĭisplay a text message at the console (to standard error).ĭisplay string string on standard error before output, any metacharacters in string are expanded. Use "checkpoints": display a progress message every NUMBER records (default 10).Įxecute ACTION at every checkpoint. This is the default behavior.ĭo not check device numbers when creating incremental archives. If not specified, backup-method defaults to the value of environment variable VERSION_CONTROL if VERSION_CONTROL is undefined, backup-method defaults to existing.Ĭhange to directory DIR before performing any operations.Ĭheck device numbers when creating incremental archives. Make numbered backups of files that already have them, and simple backups of the others. Rather than deleting files from the file system, tar will back them up using the specified backup method backup-method, which may be one of the following: Use BLOCKS x 512 bytes-per-record when handling the archive.
UNTAR COMMAND IN LINUX ARCHIVE
Preserve access times on archived files, either by restoring the times, or (if the operating system supports it) not changing them in the first place.ĭo not automatically determine the compression program using the archive file name suffix.
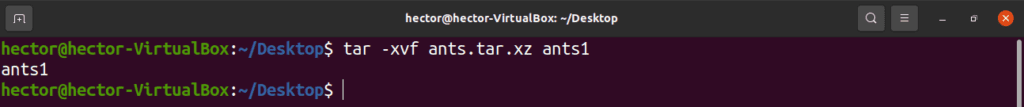
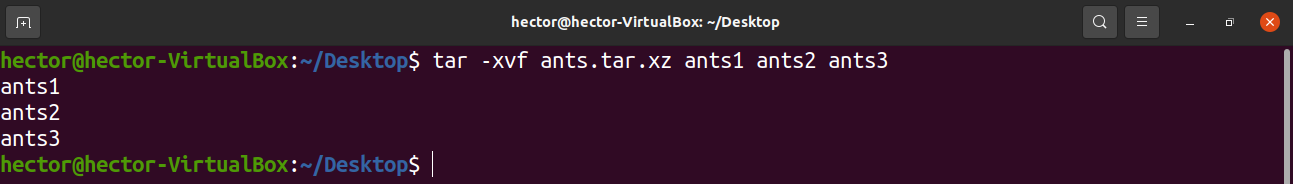
(This option is especially useful when the name of the file begins with a dash.)įile name patterns must match from the beginning of a file name.įile name patterns may match after any " /" (this is the default for excluding files see -exclude, below). tar.gz is always handled as if the -gzip option had been specified (see -gzip, below).Īdd file to the archive. For example, if this option is specified, an archive with the extension. Use the archive's suffix to determine the compression program. (If you're not sure what this means, you don't need to use this option.) The following options specify the way tar operates:. (This function doesn't work on magnetic tapes).Īppend files to the end of a tar archive.Īppend files, but only those that are newer than the copy in the archive. Specifying one of the following functions selects what tar's main mode of operation will be: A, -catenate,Ĭalculate any differences between the archive and the file system.ĭelete from the archive. With the long form, they may be given by appending " = value" to the option.įor example, the following commands are all equivalent: tar -create -file=archive.tar file1 file2 tar -c -f archive.tar file1 file2 tar -cf archive.tar file1 file2 tar cf archive.tar file1 file2 Functions
Some options take a parameter with the single-letter form these must be given as separate arguments. A long function name must be prefixed with a double dash (" -"). A function letter does not need to be prefixed with a dash (" -"), and may be combined with other single-letter options.
The first argument to tar should be a function specification: either one of the letters A, c, d, r, t, u, or x, or one of the long function names. delete | r -append | t -list | -test-label | u -update | Syntax tar A -catenate -concatenate | c -create | d -diff -compare | This documentation covers the GNU version of tar, which is included with most modern variants of the Linux operating system. It was later formalized as part of the POSIX standard, and today is used to collect, distribute, and archive files, while preserving file system attributes such as user and group permissions, access and modification dates, and directory structures. Tar was originally developed in the early days of Unix for the purpose of backing up files to tape-based storage devices.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
